Why does robustness testing matter more than peak performance?
Robustness Testing
System Reliability
Tech Systems
Peak performance can be impressive, but it is not synonymous with reliability. A model that excels under controlled laboratory conditions may degrade quickly when exposed to real-world variability.
Robustness testing evaluates how well a system performs under distribution shifts, edge cases, and environmental noise. It measures durability, not just optimal output.
Why Robustness Testing Matters
Controlled benchmarks capture best-case performance. Real-world deployment introduces variability in language, context, demographics, and environment.
For a Text-to-Speech (TTS) system, this may include accent diversity, informal phrasing, background interference, or domain-specific vocabulary. Robustness testing ensures stability across these dimensions rather than selective excellence.
Core Reasons to Prioritize Robustness Testing
1. Real-World Reliability: Models must function across unpredictable user inputs and diverse interaction patterns. Robustness testing simulates deployment variability to validate stability.
2. Edge Case Exposure: Rare phrases, unusual prompts, or atypical speech structures often reveal hidden weaknesses. Testing against such cases prevents silent deployment failures.
3. Trust Preservation: Consistent performance across contexts strengthens user confidence, particularly in sensitive sectors such as healthcare.
4. False Confidence Prevention: High benchmark scores can conceal fragility. Robustness testing uncovers performance gaps that controlled evaluation may not reveal.
5. Continuous Adaptation: Real-world conditions evolve. Ongoing robustness validation enables models to adapt without performance erosion.
Practical Implementation Principles
Scenario-Based Stress Testing: Define realistic and adverse usage conditions that reflect deployment environments.
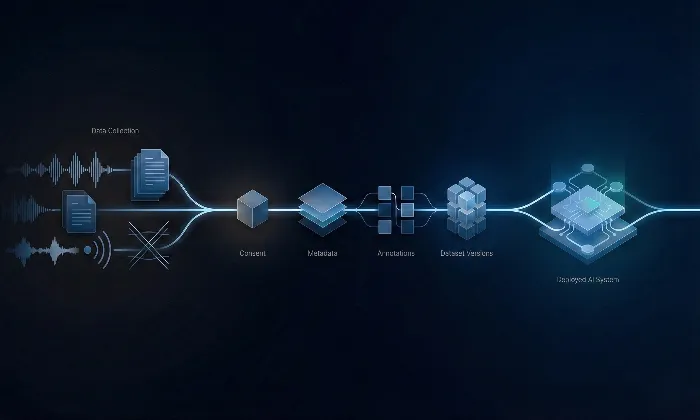
Diverse Dataset Inclusion: Integrate varied speech patterns, dialects, and contextual prompts during evaluation.
Human Perceptual Validation: Combine quantitative stress metrics with structured human evaluation to detect subtle degradation in naturalness or tone.
Longitudinal Monitoring: Reassess robustness after updates, retraining cycles, or data refreshes to detect drift early.
Practical Takeaway
Peak performance reflects capability under ideal conditions. Robustness reflects reliability under real conditions.
Sustainable AI deployment requires both, but robustness determines long-term success.
At FutureBeeAI, evaluation frameworks are designed to test stability under distribution shifts, edge cases, and perceptual variability, ensuring models perform consistently beyond controlled benchmarks.
What Else Do People Ask?
Related AI Articles
Browse Matching Datasets
Acquiring high-quality AI datasets has never been easier!!!
Get in touch with our AI data expert now!