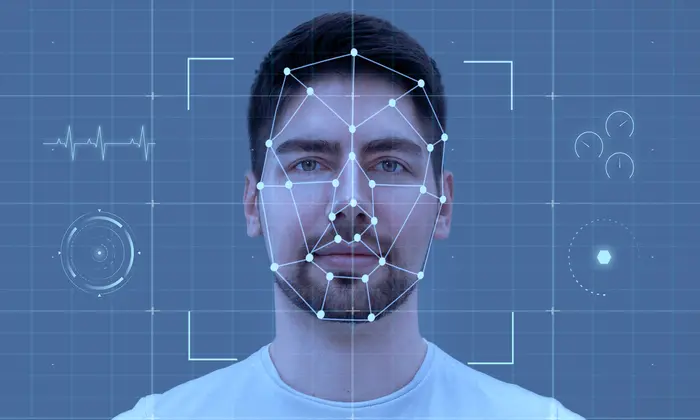
How do lighting conditions affect face detection accuracy?
Face Detection
Computer Vision
Image Processing
Lighting is often underestimated in face detection, yet it is one of the most influential factors affecting accuracy. For AI practitioners, lighting is not a minor technical variable, it is a core challenge that can determine whether a system performs reliably in real-world environments or fails outside controlled conditions.
Understanding how lighting interacts with face detection models is essential for building systems that work consistently across deployment scenarios.
Key Lighting Challenges in Face Detection
Face detection systems rely on visible facial structure and contrast. Variations in lighting can distort or obscure these signals, leading to missed detections or false results.
Brightness Levels: Underexposed images reduce visible detail, making it difficult to detect eyes, nose, and mouth accurately. Overexposed images can wash out these same features, causing detection failures or false negatives.
Light Direction: The direction of light strongly influences facial geometry. Frontal lighting generally supports better detection, while side or top lighting introduces shadows that hide facial contours and confuse detection models.
Color Temperature: Different light sources, incandescent, fluorescent, LED, or natural daylight, alter color representation and skin tone appearance. These shifts complicate detection, especially when models are trained on narrow lighting distributions.
Why Lighting Variability Matters
Lighting challenges have downstream effects that extend beyond raw detection accuracy:
Model Robustness: Models trained primarily in controlled lighting environments often fail in real-world settings where illumination is inconsistent. This directly impacts applications like identity verification and access control.
Data Quality and Bias: If diverse lighting conditions are not included during dataset creation, models become biased toward “ideal” conditions and underperform elsewhere.
Operational Costs: Lighting-related detection failures increase manual verification, retraining cycles, and system friction driving up operational costs and degrading user experience.
Practical Strategies for AI Teams
1. Diverse Dataset Collection:
Intentionally collect images and videos across a wide lighting spectrum, indoor artificial light, outdoor daylight, low-light environments, and mixed lighting conditions. Reviewing comprehensive facial datasets helps ensure adequate coverage.
2. Controlled Stress Testing:
Evaluate face detection performance under systematically varied lighting scenarios. Identifying failure points early allows teams to correct dataset gaps or model weaknesses before deployment.
3. Adaptive Algorithm Techniques:
Incorporate preprocessing and normalization techniques to reduce lighting sensitivity. Methods such as histogram normalization and illumination correction often supported during image annotation help models maintain consistency under changing light.
Practical Takeaway
Lighting is not just an environmental detail, it is a foundational factor in face detection accuracy. Systems that ignore lighting diversity will inevitably fail in real-world conditions.
By prioritizing lighting variation in data collection, testing models under realistic illumination, and applying adaptive algorithms, AI teams can build face detection systems that are resilient, scalable, and dependable.
Proactively addressing lighting challenges improves not only technical performance, but also operational reliability and user trust in production environments.
What Else Do People Ask?
Related AI Articles
Browse Matching Datasets
Acquiring high-quality AI datasets has never been easier!!!
Get in touch with our AI data expert now!